What is Penile Cancer?
Penile cancer is a rare condition which occurs when malignant (cancerous) cells form in the tissue of the penis.
If you are over 50 and uncircumcised, you are most at risk of getting penile cancer. If you have a history of genital warts and human papillomavirus (HPV or the wart virus) you are also at higher risk.
Discuss any penile changes with your doctor. If you have penile cancer, your partner should also be screened for other forms of cancer caused by HPV in the genital area – this includes cervical, vulvar and anal cancer.
What are the signs and symptoms of Penile Cancer?
- An area of skin becoming thicker.
- Changes in the skin color.
- A lump.
- An ulcer (sore) that might bleed.
- A reddish, velvety rash under the foreskin.
- Small, crusty bumps.
- Flat, bluish-brown growths.
- Smelly discharge (fluid) or bleeding under the foreskin.
What Is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer begins when cells in the prostate gland start to grow out of control. The prostate is a gland found only in males. It makes some of the fluid that is part of semen.
The prostate is below the bladder (the hollow organ where urine is stored) and in front of the rectum (the last part of the intestines). Just behind the prostate are glands called seminal vesicles that make most of the fluid for semen. The urethra, which is the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body through the penis, goes through the center of the prostate.
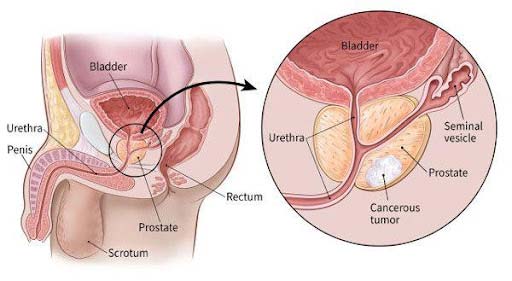
Prostate cancer rarely occurs in those younger than 55. Those who develop prostate cancer are mostly over the age of 65. In the very elderly, prostate cancer often grows very slowly and may cause no symptoms.
If you are over 45, you should discuss with your doctor whether to have prostate cancer screening.
What are the symptoms and signs of prostate cancer?
- Frequent urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow or the need to strain to empty the bladder
- The urge to urinate frequently at night
- Blood in the urine
- New onset of erectile dysfunction
- Pain or burning during urination, which is much less common
- Discomfort or pain when sitting, caused by an enlarged prostate
What Is Testicular Cancer?
Testicular cancer is a disease that occurs when cancerous (malignant) cells develop in the tissues of a testicle. The development of cancerous cells in both testicles can occur, but is very rare.
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer in those between 15 and 35 years but it can happen at any age.
Testicular cancer is almost always curable, particularly if it is diagnosed and treated at an early stage.
To catch this cancer early, men are encouraged to learn about early signs, learn how to do a testicular self-exam and talk with a health care provider if there is a suspicious lump, swelling, or pain in the area.
What are the Symptoms?
Signs of a testicular tumor are:
- A painless lump in the testicle (the most common sign)
- Swelling of the testicle (with or without pain) or a feeling of weight in the scrotum
- Pain or a dull ache in the testicle, scrotum or groin
- Tenderness or changes in the male breast tissue
If you find any lump or firm part of the testicle, you should see a doctor to find out if it is a tumour. Very few men who have testicular cancer felt pain at first.
.png)


